|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
ENDscript is an interface grouping eight types of programs: BLAST; MULTALIN/ CLUSTALW; DSSP; CNS; ESPript; BOBSCRIPT/ MOLSCRIPT; DINO; PHYLODENDRON; PROFIT. It aims to produce from a single PDB file four PostScript figures containing most required sequence and structure information on a protein of known structure. You just have to upload your PDB file via the interface and click on the SUBMIT button to obtain the first ESPript figure:
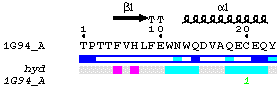
|
The resulting PostScript displays sequences of each chainID contained in the PDB file (single chain, A, in the example above, PDB code 1G94). Residue numbering is checked by SPDB, an home-made program. Secondary structure elements, calculated by DSSP, are displayed above sequence along with grey stars marking residues with alternate conformations. Relative accessibility, also calculated by DSSP, is shown below sequence by a blue-coloured bar. A second bar gives the figure of hydropathy, calculated from the sequence according to the algorithm of Kyte and Doolittle. Finally, intermolecular contacts calculated by CNS are represented by characters on the bottom line. In the example above, quotes (") highlight residues in contacts with sugar molecules and green digits (1) show disulphide bridges.
Then, you click on enable the BLAST search in the main frame of the interface and click again on SUBMIT in the buttons frame. The first monomer is kept (chain A) and a search is performed against either the PDB or the SWISSPROT database, to extract homologous sequences. Multiple alignments are executed in turn using MULTALIN or CLUSTALW. The result is sent back to ESPript, which creates a new figure with secondary structure elements, if an aligned sequence has a known 3D structure deposited with the PDB:
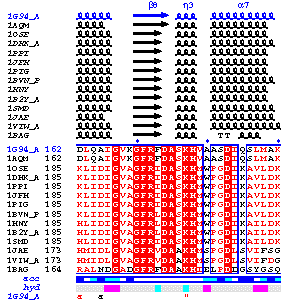
|
A command file with the location of secondary structure elements in the PDB file is also generated. It is passed to BOBSCRIPT to display the third figure below.
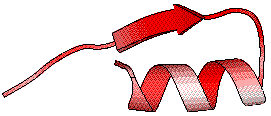
|
Similarity scores calculated from the multiple alignment are shown on this
ribbon representation of the query (1G94) by a white (low score) to
red (identity) colour ramp. In addition, a similar figure in VRML 2.0 is
created using MOLSCRIPT.
It can be viewed and rotated using a web browser (Netscape or Explorer)
if plug-ins from CORTONA or COSMO have been installed.
Click here for an example in VRML (ramp
is now from violet to red). Note that an option in ENDscript allows to display on
the figure, blue side chains corresponding to strictly conserved residues.
The program PROFIT is used to superimpose known 3D structures of homologous sequences onto the query and to calculate rms deviation by CA pairs over the fitted region. A new BOBSCRIPT figure is produced with the backbone of the query rendered as a tube, its radius being proportional to the calculated rms deviation; colour still varies from white to red according to similarity (low to high).
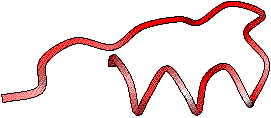
|
Thus, everything is performed automatically but the user can change most defaults via the interface.
| Introduction to the web interface | |
| Manual for ENDscript | |
| Examples on alpha amylases | |
| Execute ENDscript NOW |
You may have to configure your browser with appropriate helpers applications to display the generated output. The mime type of the PostScript file is application/postscript, it could be linked to ghostview. The mime type of generated PDB files is chemical/x-pdb, it could be linked to rasmol
Main site is Laboratoire de BioCristallographie , Institut de Biologie et Chimie des Protéines (CNRS UMR 5086) - Lyon, France.

|

|

|

|

|
|

|
|
Please, read this installation documentation to install the script of the html interface on your server (Unix or Linux-Apache).
Copyleft This software is covered by the gnu public license.